6/7/25About 595 words
Definition of Software Engineering
Software engineering is an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software.
Software contains not only the program, but also all associated documentation and configuration data.
Software Principles and Aspects
Software engineering is intended to support professional software development.
It includes techniques that support program specification, design, and evolution, none of which are normally relevant for personal software development.
Importance of Software Engineering
- The requirements of reliable and trustworthy systems are increasing nowadays. So we need to be able to produce such systems economically and quickly.
- It is usually cheaper to use software engineering methods and techniques for software systems.
- For most types of systems, the majority of costs are the costs of changing the software after it has gone into use.
Development Process
Software Development Life Cycle
- Requirement Analysis
- Planning
- System Design
- Implementation (Coding)
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance & Updates
Software Process Activities
- Software Specification
- Customers and engineers define the software that is to be produced and the constraints on its operation.
- Software Development
- Design and program the software.
- Software Validation
- The software is checked to ensure that it is what the customer requires.
- Software Evolution
- Modify the software to reflect changing customer and market requirements.
Software Evolution
- Software development does not stop when a system is delivered but continues throughout the lifetime of the system.
- It inevitably has to change if it is to remain useful after deploy.
- Software evolution may be triggered by,
- Changing business requirements
- Reports of software defects
- Change to other systems
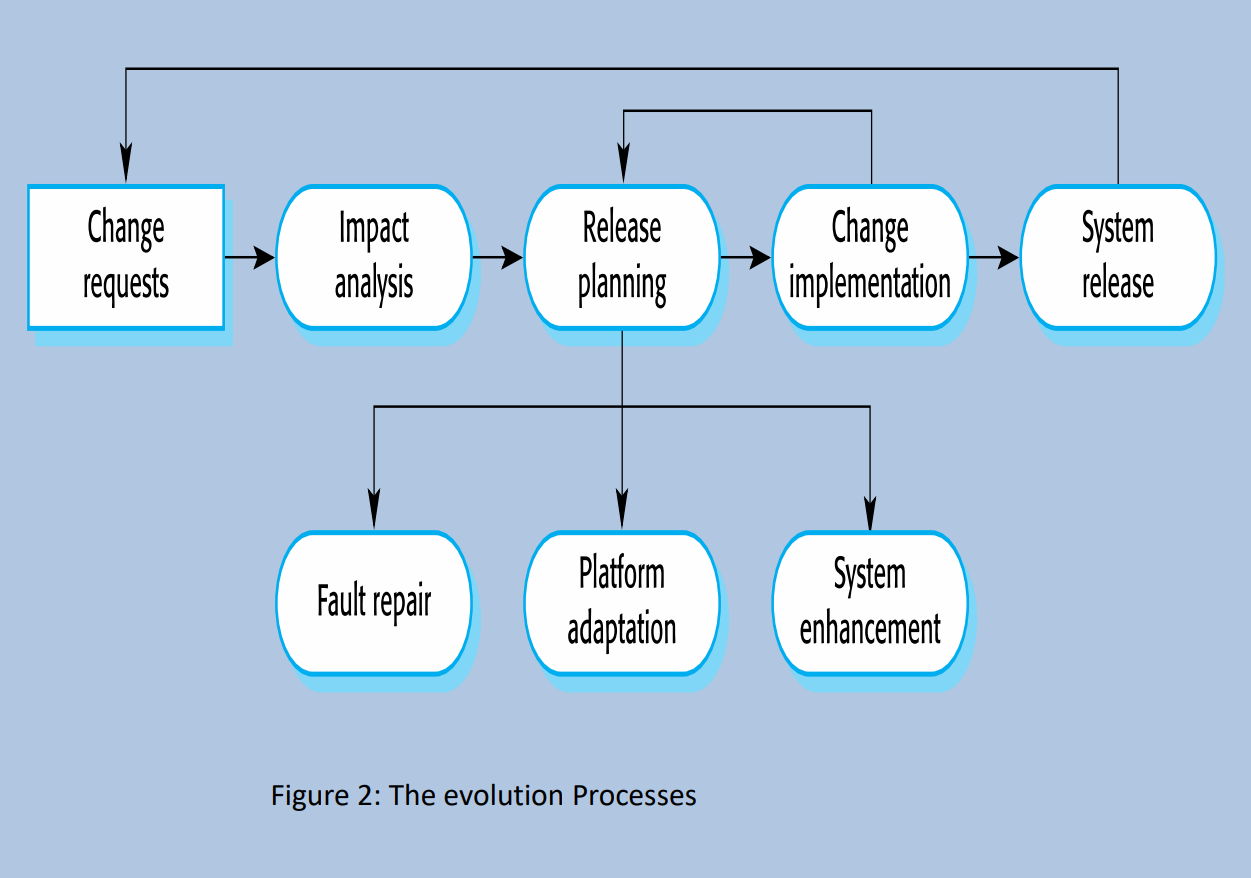
Evolution Processes
- System change proposals are the driver for system evolution in all organizations.
- Change proposals may come from
- existing requirements that have not been implemented
- request of new requirements
- bug report
- new ideas
- Change proposals may come from
- The changes are implemented and validated, then a new version of the system is released.
3 Reasons for the Urgent Changes
- A serious system fault occurs that has to be repaired to allow normal operation to continue.
- Changes to the systems operating environment have unexpected effects that disrupt normal operation.
- There are unanticipated changes to the business running the system.
Software Engineering Diversity
- There are many different types of software system, and there is no universal set of software techniques that is applicable to all of these.
- The software engineering methods and tools used depend on the type of application being developed, the requirements of the customer and the background of the development team.
Software Engineering Fundamentals
- Systems should be developed using a managed and understood development process.
- Dependability and performance are important for all types of system.
- Understanding and managing the software specification and requirements are important.
- Reuse software that has already been developed instead of writing new software.
Types of Software Engineering
Internet Software Engineering
- Web services allow application functionality to be accessed over the web.
- Cloud computing is an approach to the provision of computer services where applications run remotely on the
cloud. - Users do not buy software but pay according to use.
Web-based Software Engineering
- Web-based systems are complex distributed systems.
Web Software Engineering
- Software Reuse
- It is the dominant approach for constructing web-based systems.
- Incremental and Agile Development
- Web-based systems should be developed and delivered incrementally.
- Service-oriented Systems
- Software components are stand-alone web services.
- Rich Interfaces
