6/8/25About 222 words
Rational Unified Process
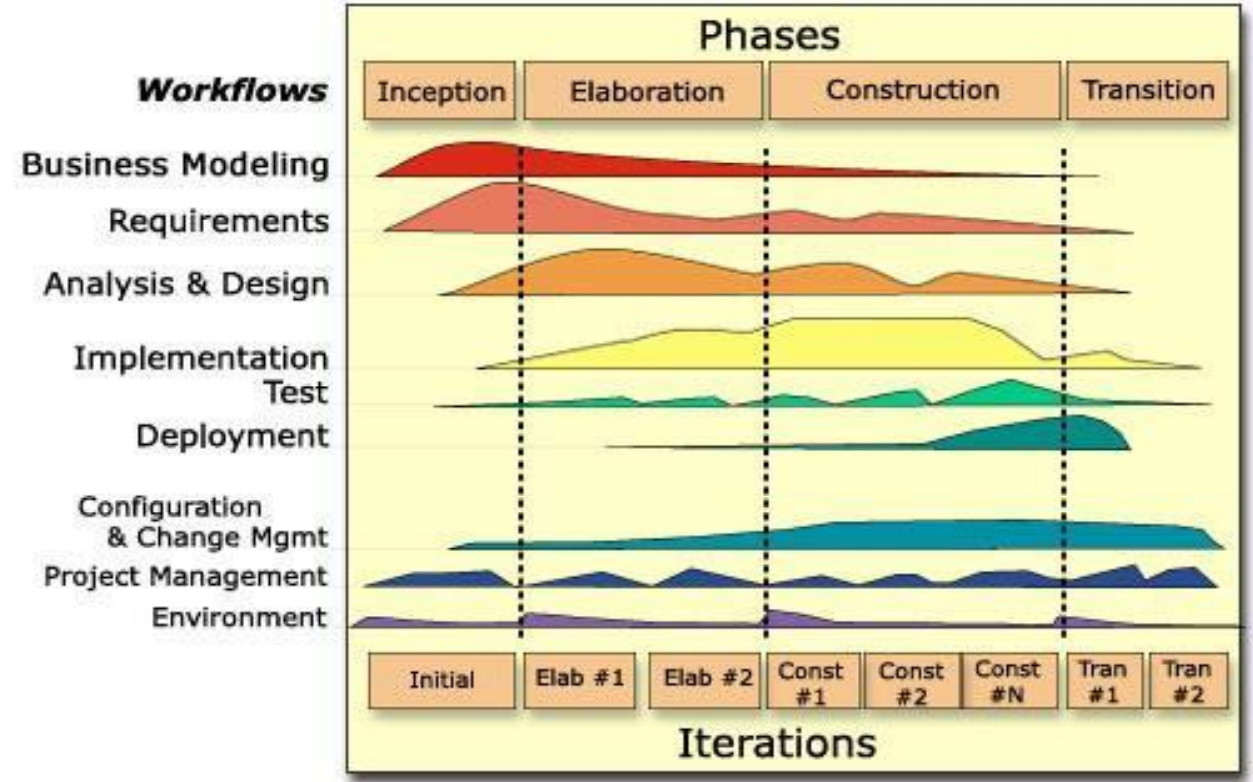
- It brings together elements from all the generic models and supports prototyping and incremental delivery.
- Rational Unified Process is normally described from 3 perspectives:
- A dynamic perspective shows the phases of the model over time.
- A static perspective shows the process activities that are enacted.
- A practice perspective suggests good practices to be used during the process.
Workflow
- Business Modelling: The business process are modelled using business use cases.
- Requirements: Actors who interact with the system are identified and use cases are developed to model the system requirements.
- Analysis and Design: A design model is created and documented using architectural models, component models, object models, and sequence models.
- Implementation: The components in the system are implemented and structured into implementation sub-systems.
- Testing: It is an iterative process that is carried out in conjunction with implementation. System testing follows the completion of the complementation.
- Deployment: A product release is created, distributed to users and installed in their workplace.
- Configuration and Change Management: Support workflow managed changes to the system.
- Project Management: Support workflow manages the system development.
- Environment: This workflow is concerned with making appropriate software tools available to the software development team.
